Book a Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige Today
People with Certain Medical Conditions
Individuals with Gastrointestinal Issues
Individuals with certain medical conditions may want to avoid dermal fillers. It’s crucial to consult with a qualified medical professional to determine if fillers are safe for you.
People with active skin infections or inflammation near the injection site should avoid fillers. The filler can worsen the infection and complicate treatment.
Individuals with bleeding disorders or those taking blood thinners may be at increased risk of bruising or bleeding after filler injections.
Patients with autoimmune diseases, such as lupus or scleroderma, may experience complications from fillers due to their immune system’s reactivity.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should generally avoid dermal fillers until more research is available on the potential risks to themselves and their babies.
People with certain facial conditions, such as Bell’s palsy or a history of facial paralysis, may want to consult with a specialist to assess the risks and benefits of filler injections in their specific case.
Individuals with gastrointestinal issues who are considering fillers should speak to their doctor. While there isn’t a direct link between gastrointestinal problems and filler complications, some conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or Crohn’s disease can affect the body’s overall inflammatory response, potentially influencing how one heals from injections.
It is essential to provide a complete medical history to your doctor before any cosmetic procedure, including filler injections.
Those Experiencing Allergies or Sensitivities
Book a Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige Today
People with certain medical conditions may need to avoid dermal fillers.
These conditions can include:
active infections at the injection site or elsewhere in the body
blood clotting disorders
autoimmune diseases such as lupus or scleroderma
a history of keloid scarring
Certain medications, such as blood thinners, can also increase the risk of complications from fillers.
Individuals with allergies or sensitivities should also be cautious about dermal fillers.
Reactions can range from mild redness and swelling to more serious allergic reactions.
It’s important to inform your doctor of any known allergies, especially to lidocaine (a local anesthetic often used in conjunction with fillers) or hyaluronic acid (the most common type of filler).
Always consult with a qualified medical professional to determine if dermal fillers are right for you and to discuss any potential risks or contraindications based on your individual health history.
Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women
Potential Risks to Fetal Development
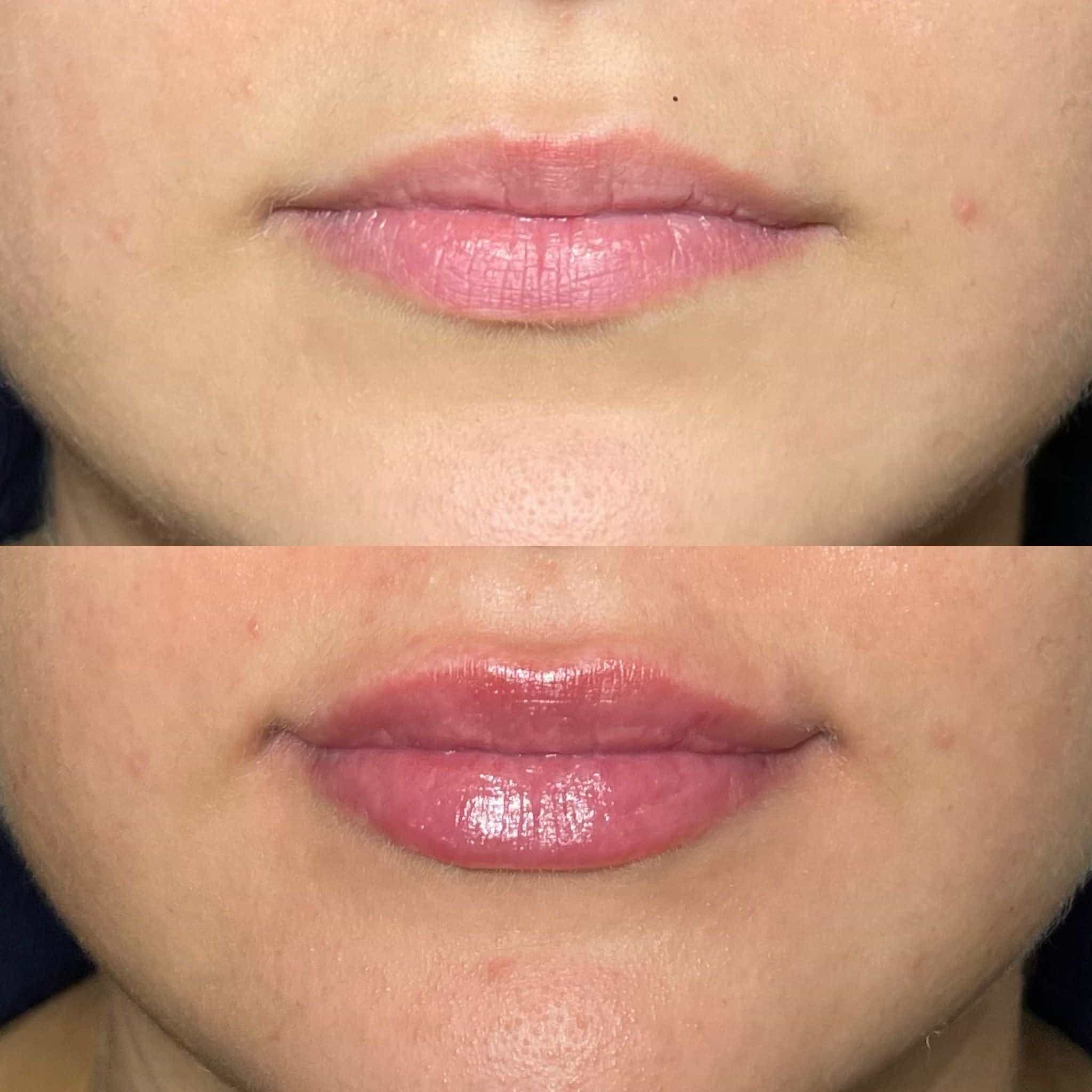
Pregnant or breastfeeding women are often advised to avoid dermal fillers due to potential risks to fetal development and insufficient research on their safety during these crucial periods.
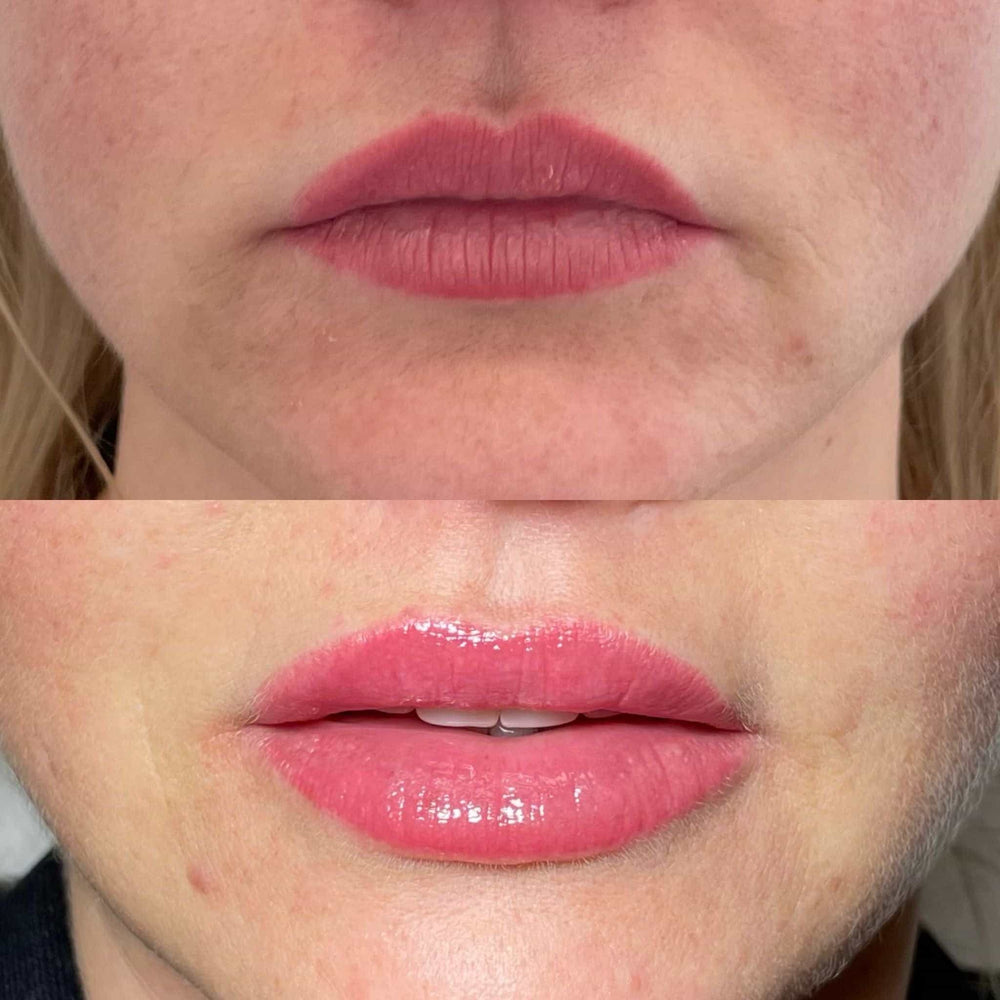
While fillers themselves don’t directly enter the bloodstream in large quantities, some ingredients can be absorbed into the body. This absorption could potentially expose the fetus or nursing infant to substances whose long-term effects are unknown.
One concern is hyaluronic acid, a common filler ingredient. While generally considered safe, its impact on fetal development hasn’t been extensively studied.
Another concern is the risk of inflammation or allergic reactions at the injection site. These reactions could potentially affect placental blood flow or interfere with milk production.
The decision to use dermal fillers during pregnancy or breastfeeding should be made in consultation with a qualified healthcare professional who can weigh the potential risks and benefits in each individual case.
Given the lack of conclusive evidence regarding safety, it’s generally recommended that pregnant and breastfeeding women err on the side of caution and avoid dermal fillers until more research is available.
Effects on Breast Milk Composition
Pregnant and breastfeeding women are particularly sensitive to the potential effects of fillers on their health and, importantly, the composition of their breast milk.
Here’s a detailed look at how fillers might affect them:
-
Potential Transfer to Breast Milk: Fillers can potentially cross into breast milk. While the extent of transfer varies depending on the type of filler, its chemical structure, and individual factors, it’s essential to minimize potential risks to the nursing infant.
-
Infant Sensitivity: Breastfed infants have developing immune systems and may be more susceptible to the effects of foreign substances introduced through breast milk. Fillers might cause allergic reactions or digestive issues in sensitive babies.
-
Hormonal Disruption: Some fillers contain chemicals that can mimic hormones or interfere with hormonal balance. This could potentially affect both the mother’s and infant’s hormone regulation, leading to unforeseen consequences.
It’s crucial for pregnant and breastfeeding women to be informed about the potential risks associated with fillers and to discuss any concerns with their healthcare providers. They can help assess individual risk factors and provide guidance on safer alternatives.
Children and Adolescents
Developing Digestive Systems
Children and adolescents are still developing their digestive systems.
During infancy, the digestive tract undergoes significant changes as it matures and learns to process various foods. The small intestine lengthens, enzymes become more efficient, and the gut microbiome begins to establish itself.
This developmental stage can make children and adolescents more susceptible to digestive issues. Their systems might struggle to break down certain components in fillers, leading to discomfort or other complications.
For example, some fillers like wheat flour or corn starch could be difficult for young individuals with developing digestive tracts to digest completely.
This can contribute to bloating, gas, and even constipation.
Additionally, the immune systems of children are still maturing, making them more vulnerable to sensitivities and allergic reactions to certain filler ingredients.
It’s important to note that individual tolerance varies greatly.
Some children may digest fillers without any issues, while others experience adverse effects.
Parents and guardians should pay attention to their child’s digestive response to different foods and consider avoiding fillers as a precautionary measure, especially for infants, toddlers, and children with known digestive sensitivities.
Consulting a pediatrician or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on appropriate dietary choices for growing children and adolescents.
Impact on Growth and Nutrition
Children and adolescents are in periods of rapid growth and development, making their nutritional needs particularly crucial. Proper nutrition during these years directly impacts physical growth, cognitive development, and overall health.
Adequate protein intake is essential for building and repairing tissues, supporting muscle growth, and developing strong bones.
Carbohydrates provide the primary source of energy for the body, fueling growth processes and brain function.
Healthy fats are crucial for hormone production, brain development, and nutrient absorption.
Micronutrients like vitamins and minerals play diverse roles in supporting various bodily functions, including immunity, bone health, and cognitive development.
Inadequate nutrition during childhood and adolescence can have long-lasting consequences. Stunting, a condition characterized by impaired linear growth, is a significant concern associated with malnutrition.
Nutritional deficiencies can lead to delayed puberty, weakened bones, impaired immune function, and increased susceptibility to infections.
Furthermore, poor nutrition can negatively impact cognitive development, affecting learning ability, memory, and academic performance.
Prince and Flower Electric Youth Magazine Melissa J Design Detailed Weddings LA
- Brock Yates Quotes - September 16, 2025
- Botox For Square Jaw Reduction In Ashtead, Surrey - September 13, 2025
- Botox For Bruxism In Bletchingley, Surrey - September 11, 2025
