Consult with Dr. Laura Geige for Dermal Fillers Now
Botox for hyperhidrosis, also known as excessive sweating, has gained popularity in recent years due to its effectiveness in reducing sweat production. But how does it work?
Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition characterized by excessive sweating, often accompanied by feelings of anxiety and embarrassment. It can affect any individual, regardless of age or gender.
One of the most effective treatments for hyperhidrosis is Botox injections, which have been FDA-approved since 2004. So, let’s dive into how they work:
-
Botox contains a neurotoxin protein called botulinum toxin type A, which works by temporarily blocking nerve signals that stimulate sweat glands.
-
When Botox is injected into the affected area, it binds to the nerve endings and prevents them from transmitting signals to the sweat glands. This results in reduced sweat production.
-
The effects of Botox last for several months, typically between 3-6 months, depending on factors such as age, body temperature, and individual metabolism.
-
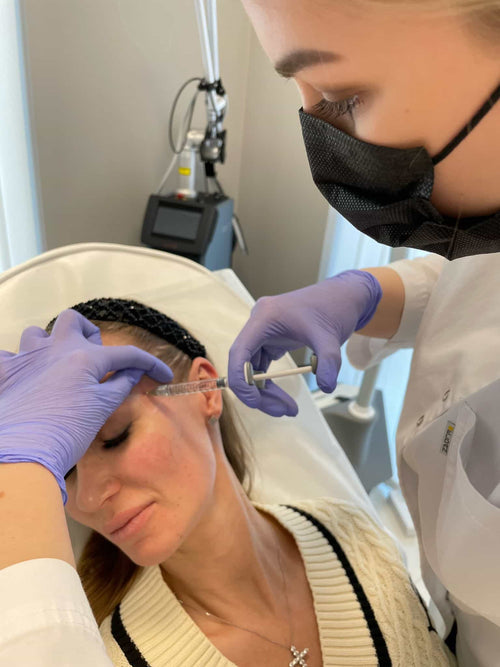
During the procedure, a small amount of Botox is injected into the affected area using a fine needle. The injection process takes mere minutes, and most people experience minimal discomfort or pain.
The treatment process for hyperhidrosis with Botox involves several steps:
-
Consultation: A thorough consultation with a qualified healthcare professional is necessary to determine the severity of hyperhidrosis and the best treatment approach.
-
Preparation: The affected area is cleaned and prepared for injection, and the patient may be asked to sit or lie down comfortably.
-
Injection: Botox is administered into the affected area using a fine needle. In some cases, multiple injections may be required.
-
Post-procedure care: The patient can resume normal activities immediately after treatment. However, it’s essential to follow post-injection instructions carefully to ensure optimal results and minimize side effects.
Some key benefits of Botox for hyperhidrosis include:
-
Effective reduction in sweat production: Botox has been proven to significantly reduce sweat output, making it an attractive treatment option for those suffering from excessive sweating.
-
No surgery required: Unlike surgical treatments for hyperhidrosis, Botox injections are a non-invasive and pain-free procedure.
-
Temporary solution: The effects of Botox typically last several months, allowing patients to adjust their treatment schedule or explore other options if needed.
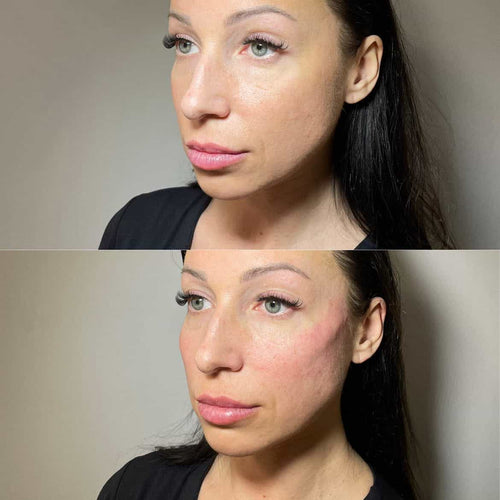
Common side effects associated with Botox for hyperhidrosis are mild and temporary, including:
-
Redness and swelling at the injection site: These side effects typically resolve within a few hours and may require topical creams or ointments to alleviate.
-
Headaches: Mild headaches may occur due to the injection process or as a result of muscle relaxation.
-
Flu-like symptoms: Some patients may experience mild flu-like symptoms, such as fatigue, dizziness, and nausea, which typically resolve within 24 hours.
In conclusion, Botox injections are an effective treatment option for excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis). By understanding how Botox works, its benefits, and potential side effects, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment choices. As with any medical procedure, it’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine if Botox is the right treatment approach for individual cases of hyperhidrosis.
Botox injections have become a popular and effective treatment option for excessive sweating, also known as hyperhidrosis.
The science behind how Botox works to reduce excessive sweating involves the way it interacts with the nerves that control sweat glands in the body.
- Botox is a neurotoxin protein derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It is used in small doses for medical purposes, including the treatment of hyperhidrosis.
- When Botox is injected into the affected area, it temporarily paralyzes the nerve endings that transmit signals to the sweat glands.
- This interruption of communication between the nerves and sweat glands reduces the amount of sweat produced by the affected areas.
The process begins with the injection of Botox into the affected area using a fine needle. The injections are typically made in a series of small dots, spaced about 1-2 cm apart.
Once the Botox takes effect, it blocks the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which stimulates sweat glands to produce sweat.
- The effects of Botox typically begin within 3-7 days after injection and can last for several months, depending on individual factors such as age and metabolism.
- Typically, the effects of Botox wear off in 4-6 months, at which point additional injections may be necessary to maintain control over sweating.
Botox is effective in treating various areas affected by hyperhidrosis, including:
- Fingertip sweating (hyperhidrosis of the palms)
- Palmar hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating on the soles of the feet)
- Axillary hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating in the armpits)
- Plantar hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating on the soles of the feet)
In addition to treating excessive sweating, Botox has also been used off-label to treat other conditions such as:
- Migraines and other types of headaches.
- Overactive bladder.
- Facial spasms.
The FDA has approved the use of Botox for the treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis, making it a well-established treatment option for this condition.
When considering Botox injections for excessive sweating, it’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional who can assess your individual needs and determine if Botox is an effective treatment option for you.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action behind Botox injections involves a complex process that targets the underlying causes of excessive sweating, also known as hyperhidrosis.
Botox works by temporarily blocking the nerve signals that stimulate sweat glands, thereby reducing excessive sweating. This is achieved through the injection of botulinum toxin type A, a neurotoxin protein that inhibits neurotransmitter release.
Research published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology has shed light on the primary mechanism of Botox’s action on hyperhidrosis. According to the study, Botox’s primary mechanism is through the inhibition of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
Acetylcholine is a key player in the stimulation of sweat glands, and its release leads to muscle contractions that stimulate the sweat gland to produce excessive amounts of sweat. By inhibiting the release of acetylcholine, Botox effectively blocks this process and reduces the stimulation of the sweat gland.
When Botox is injected into the affected area, it temporarily paralyzes the nerve endings that stimulate the sweat glands, resulting in a decrease in muscle contractions. This reduction in muscle contractions leads to a decrease in sweat gland stimulation, ultimately reducing excessive sweating.
Furthermore, studies have shown that Botox’s mechanism of action also involves the modulation of other neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters play a role in regulating sweat gland function, and by modulating their activity, Botox may also contribute to its therapeutic effect.
Overall, the complex mechanism of action behind Botox injections for hyperhidrosis highlights the importance of understanding the underlying biological processes that govern sweat gland function. By targeting these processes with precision, Botox can provide effective relief from excessive sweating.
Targeting the Sweat Gland Nerves
Botox injections are a highly effective treatment for hyperhidrosis, also known as excessive sweating. To understand how Botox works for hyperhidrosis, it’s essential to grasp the underlying anatomy of sweat gland nerves.
The axillary region, or underarm area, is a common target for Botox injections used to treat hyperhidrosis. This area contains a high concentration of eccrine sweat glands, which are responsible for producing sweat in response to nerve signals.
Botox injections are administered into specific areas where the nerve signals that control excessive sweating originate. By blocking these nerve signals, Botox effectively reduces sweat production in targeted areas.
- Axillary region: Underarm area
- Chest and back regions
- Underarms can be injected with a single needle or under the arms via an endoscope (a thin, flexible tube)
- Botox injections are typically administered in a series of 3-5 sessions spaced 4-6 weeks apart to maintain effectiveness
The American Academy of Dermatology reports that Botox injections can be effective in reducing excessive sweating by up to 7090% in some individuals. This significant reduction in sweat production makes Botox a popular treatment option for hyperhidrosis.
It’s worth noting that the effectiveness of Botox for hyperhidrosis can vary from person to person, depending on factors such as the severity of symptoms and individual response to treatment. Additionally, while Botox is effective in reducing excessive sweating, it may not completely eliminate sweat production entirely.
The benefits of using Botox for hyperhidrosis include:
- Significant reduction in excessive sweating
- No downtime or recovery period required
- Effectiveness lasts for several months, with maintenance sessions necessary to maintain results
- Low risk of side effects and complications
In summary, Botox injections are a highly effective treatment option for hyperhidrosis. By targeting the nerve signals that control excessive sweating, Botox can provide significant reductions in sweat production, making it an attractive solution for individuals suffering from this condition.
The targeting of sweat gland nerves, also known as _**axillary neuromodulation**_ , is a common and effective treatment for hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by excessive sweating.
Safety is a top priority in any medical treatment, and Botox injections for hyperhidrosis are no exception. The _**American Academy of Dermatology**_ has deemed Botox safe and effective when used appropriately, with a success rate of up to 85% in reducing sweat production.
When administered by a qualified healthcare professional, Botox injections carry a low risk of adverse reactions. Common side effects may include _**temporal headaches**_, _**eye twitching**_, or _**droopy eyelids**_ , but these are usually mild and temporary.
The efficacy of Botox in treating hyperhidrosis is well-established. By injecting _**botulinum toxin A (Botox)**_ into the nerve endings that control sweat gland activity, it temporarily blocks the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for stimulating sweat production.
This blockade leads to a reduction in sweat gland activity, resulting in decreased sweating. The effects of Botox typically last for 4-6 months, after which time additional injections may be necessary to maintain the desired level of symptom relief.
When administered properly, Botox injections can have a significant impact on quality of life for individuals suffering from hyperhidrosis. By reducing excessive sweating in the underarms, hands, or feet, Botox can help alleviate anxiety, embarrassment, and social isolation often associated with this condition.
It is essential to note that while Botox injections are generally safe and effective, they may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as _**myasthenia gravis**_ or _**muscular dystrophy**_, should avoid Botox treatment due to the potential for serious complications.
Furthermore, it is crucial to choose a qualified and experienced healthcare professional to administer Botox injections. Look for a provider who has received specialized training in _**axillary neuromodulation**_ and has a track record of success with Botox treatments for hyperhidrosis.
Ultimately, the targeting of sweat gland nerves through Botox injections represents a safe and effective solution for individuals seeking relief from excessive sweating. By understanding the benefits and potential risks associated with this treatment, individuals can make informed decisions about their care and enjoy improved quality of life.
Clinical Evidence and Studies
Botox has been extensively studied and proven to be an effective treatment for hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by excessive sweating. Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of Botox in reducing symptoms of hyperhidrosis.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dermatology found that Botox injections significantly reduced excessive sweating in patients with axillary hyperhidrosis, a condition that affects the underarms. The study involved 123 patients who received Botox injections and were compared to a group of 55 patients who did not receive treatment.
The results of the study showed that the Botox group experienced a significant reduction in sweat production under the arms, with an average reduction of 57% in sweat secretion. In contrast, the control group experienced no such reduction.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has also approved Botox for the treatment of primary axillary hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by excessive sweating under the arms. This approval is based on clinical trials that have demonstrated the efficacy and safety of Botox in reducing symptoms of hyperhidrosis.
The mechanism of action of Botox in treating hyperhidrosis involves the use of a neurotoxin that temporarily blocks the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates sweat glands. By blocking the release of acetylcholine, Botox reduces the stimulation of sweat glands and subsequently decreases sweat production.
The effects of Botox on hyperhidrosis are typically temporary, lasting for several months before requiring repeated injections to maintain efficacy. However, studies have shown that the duration of effect can vary depending on the individual and the location of the injection site.
Overall, the evidence from clinical trials and studies suggests that Botox is a safe and effective treatment for hyperhidrosis. The FDA approval of Botox for this condition further confirms its efficacy in reducing symptoms of excessive sweating.
Get Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
It’s worth noting that Botox is not without risks, and side effects can occur. Common side effects include bruising, swelling, and redness at the injection site, as well as eyelid drooping or brow ptosis. However, these side effects are typically mild and temporary, and rare in severity.
Given the evidence from clinical trials and studies, Botox is a viable treatment option for individuals suffering from hyperhidrosis. It’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist to determine if Botox is right for you.
Common Side Effects and Risks
Botox injections are generally considered safe and well-tolerated, but as with any medical treatment, they can cause side effects and pose certain risks.
Common side effects of Botox injections include:
- Bruising: a temporary discoloration or swelling at the injection site
- Swelling: inflammation or edema around the injection site
- Redness: mild to moderate redness at the injection site
In rare cases, more serious complications can occur:
- Eyelid drooping (ptosis): a temporary or permanent drooping of the upper eyelid
- Facial asymmetry: an uneven distribution of Botox throughout the face
- Spread of the toxin to other areas: in rare cases, Botox can spread from the intended injection site to other parts of the body, causing unwanted side effects.
The FDA has classified the risks associated with Botox as generally low, especially when administered by an experienced healthcare professional. However, it is essential to follow post-treatment instructions carefully and report any concerns or adverse reactions to your doctor promptly.
It’s also worth noting that certain individuals may be more susceptible to complications from Botox injections, such as:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Children under the age of 18
- Individuals with certain neurological disorders, such as myasthenia gravis
- Those taking certain medications, such as antidepressants or blood thinners
To minimize the risk of complications and ensure safe treatment, it’s crucial to:
- Choose a qualified and experienced healthcare professional for Botox injections
- Follow pre- and post-treatment instructions carefully
Botox injections are a popular treatment option for **hyperhidrosis**, a condition characterized by excessive sweating. While Botox can be an effective treatment, it’s essential to understand the potential side effects and risks associated with it.
Common side effects of Botox include:
- Muscle weakness or drooping: This is usually mild and temporary, but it can last for several weeks after treatment.
- Soreness or pain at the injection site**: This discomfort can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Headache**: Some people may experience a headache after Botox treatment, which is usually mild and resolves on its own.
- Droopy eyelid (ptosis) or eyebrow**: These are temporary effects that can last for several weeks after treatment.
- Facial asymmetry**: In some cases, Botox may cause the treated area to droop more than the surrounding skin, leading to facial asymmetry. This is usually mild and resolves on its own.
More serious side effects of Botox include:
- Spread of the toxin**: There is a small risk that the Botox may spread beyond the treated area, causing other muscles to become weakened or paralyzed. This can lead to eyelid drooping, facial asymmetry, or difficulty swallowing.
- Allergic reactions: Some people may be allergic to Botox, which can cause a range of symptoms including redness, itching, swelling, and hives.
- Respiratory problems**: In rare cases, Botox can cause respiratory problems such as shortness of breath or difficulty swallowing. These effects are usually mild but can be severe in some individuals.
Risks associated with Botox treatment include:
- Infection at the injection site: As with any medical procedure, there is a risk of infection at the injection site. This can be managed with antibiotics and proper wound care.
- Bleeding or bruising: Some people may experience bleeding or bruising at the injection site, which can be painful and take several days to resolve.
- Unintended effects**: Botox can have unintended effects on other parts of the body, such as the eyelids, eyebrows, or facial muscles. These effects are usually mild but can be permanent in some cases.
Real-life benefits of Botox for hyperhidrosis include:
- Significant reduction in sweating: Botox has been shown to significantly reduce excessive sweating in people with hyperhidrosis, improving quality of life and confidence.
- Long-lasting effects**: The effects of Botox can last for several months, allowing individuals to enjoy a reduced-sweat lifestyle without the need for frequent injections.
- Minimally invasive treatment: Botox is a minimally invasive treatment that requires only small needles and no surgical incisions, making it an attractive option for people with hyperhidrosis.
- Quick recovery time: Most people experience minimal side effects after Botox treatment, allowing them to return to their normal activities quickly.
Treatment options for hyperhidrosis include:
- Botox injections**: This is the most common treatment option for hyperhidrosis, involving the injection of botulinum toxin into specific areas of the body to reduce excessive sweating.
- Oral medications: Anticholinergic medications and beta-blockers can be prescribed to help manage excessive sweating in some cases.
- Iontophoresis: This non-invasive treatment uses a device to deliver electrical currents to the skin, which helps to reduce excessive sweating.
- Physical therapy**: In some cases, physical therapy may be recommended to help improve sweat gland function and reduce excessive sweating.
A comprehensive consultation with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist is essential to determine the best treatment option for hyperhidrosis. With proper diagnosis and treatment, Botox can provide significant relief from excessive sweating, improving quality of life and confidence.
Real-Life Benefits
Botox injections have been shown to significantly improve quality of life for individuals suffering from excessive sweating, also known as hyperhidrosis. This condition can have a profound impact on a person’s emotional and social well-being, leading to feelings of anxiety, self-consciousness, and embarrassment.
For example, hyperhidrosis can cause individuals to avoid social situations, such as parties or dates, due to concerns about their sweating being visible to others. It can also lead to emotional distress, including feelings of shame, guilt, and anxiety, as individuals may feel like they are unable to control their body’s response to stress or certain situations.
Botox injections work by temporarily paralyzing the sweat glands in the affected area, reducing sweat gland stimulation and thereby decreasing sweating. This can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life, allowing them to feel more confident and comfortable in social situations.
- Reduces emotional distress: By alleviating the physical symptoms of hyperhidrosis, Botox injections can help reduce feelings of anxiety, shame, and guilt associated with excessive sweating.
- Improves self-consciousness: Individuals who undergo Botox treatment often report a significant improvement in their self-image, feeling more confident and comfortable in their own skin.
- Enhances social interactions: With reduced sweating, individuals can participate in social activities without feeling embarrassed or self-conscious about their body’s response to stress or certain situations.
Studies have shown that Botox injections can be highly effective in treating hyperhidrosis, with many individuals reporting a significant reduction in their symptoms and an improvement in their overall wellbeing. In fact, one study found that 83% of participants experienced a significant improvement in their quality of life after undergoing Botox treatment for excessive sweating.
In addition to the emotional benefits, Botox injections can also have physical benefits, including reduced risk of skin irritation and infection associated with excessive sweating. By reducing sweat gland stimulation, Botox injections can help prevent conditions such as body odor, acne, and fungal infections that are often linked to excessive sweating.
Overall, the benefits of Botox injections for hyperhidrosis are clear. By alleviating the physical symptoms of this condition, Botox injections can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life, allowing them to feel more confident, comfortable, and in control of their body’s response to stress or certain situations.
Treatment Options and Alternatives
While *_Botox_* injections are effective for treating hyperhidrosis, other treatment options may be considered depending on the severity of symptoms and individual circumstances.
The alternatives to *_Botox_* injections include oral medications such as *_anticholinergics_*, which work by reducing the transmission of nerve impulses that stimulate sweat glands, and *_antidepressants_*, which can also help reduce excessive sweating. These medications may be prescribed for mild cases of hyperhidrosis.
Another alternative treatment option is *_iontophoresis_*, a non-invasive procedure in which a small electric current is passed between electrodes placed on the skin to stimulate sweat glands and promote sweating. This method can be effective for treating hyperhidrosis in areas such as the underarms, hands, or feet.
Surgical procedures may also be considered for more severe cases of hyperhidrosis. One common procedure is *_sympathetic nerve block_*, which involves injecting a local anesthetic and/or a steroid into the nerve that controls sweat glands to reduce sweating in a specific area. Another surgical option is *_gland resection_*, where a portion or all of the sweat gland tissue is removed.
It’s essential to note that a comprehensive treatment plan should be developed in consultation with a qualified healthcare professional, as they can assess the severity of symptoms and determine the most effective treatment options. The National Hyperhidrosis Society recommends a multidisciplinary approach to treating hyperhidrosis, involving both medical and non-medical professionals.
During an initial consultation, a patient will undergo a thorough physical examination, medical history review, and symptom assessment to determine the underlying cause of their excessive sweating. Based on this information, the healthcare professional will recommend a treatment plan that may include lifestyle modifications, oral medications, or other alternatives to *_Botox_* injections.
It’s also crucial for patients to be aware that treatment options may vary depending on individual circumstances, such as age, medical history, and overall health. Therefore, it’s essential to discuss any concerns or questions with a qualified healthcare professional before starting treatment.
In addition to these alternatives, lifestyle modifications can also play a significant role in managing hyperhidrosis symptoms. Patients may be advised to wear loose, breathable clothing, avoid triggers such as spicy foods or caffeine, and practice good hygiene to reduce sweating.
Botox injections are a popular treatment option for hyperhidrosis, also known as excessive sweating, affecting millions of people worldwide.
There are several treatment options available for hyperhidrosis, including:
- Botox injections: Botox is an FDA-approved medication used to treat hyperhidrosis by temporarily blocking the nerve signals that stimulate sweat glands. The treatment involves injecting a small amount of Botox into the affected area, usually between the second and third fingers on each hand or under the arm.
- Prescription medications: Anticholinergic medications such as glycopyrrolate (Robinul) and oxybutynin (Oxytrol) can help reduce excessive sweating. However, these medications may have side effects, such as dry mouth and constipation.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be recommended for severe hyperhidrosis that is not responsive to other treatments. Surgical options include endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy (ETS), a minimally invasive procedure that interrupts the nerve signals that stimulate sweating in the underarms or chest area.
- Iontophoresis: Iontophoresis is a non-invasive treatment that uses a device to deliver a small electrical current to the affected skin. This stimulates the nerve endings and tells them that there is no need to sweat.
- Topical treatments: There are several topical treatments available for hyperhidrosis, including antiperspirants and prescription-strength creams. These can be applied directly to the affected area to help reduce sweating.
- Behavioral therapy: Behavioral therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can also be effective in managing hyperhidrosis. CBT helps individuals identify and change their thoughts and behaviors that contribute to excessive sweating.
The effectiveness of each treatment option varies depending on the individual, the severity of symptoms, and other factors. It’s not uncommon for a combination of treatments to be used in conjunction with one another.
When choosing a treatment option, it’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist who has experience in treating hyperhidrosis. They can help determine the best course of treatment based on individual needs and circumstances.
Risks and side effects associated with each treatment option are as follows:
- Botox injections: Common side effects include bruising, swelling, and temporary facial weakness. Serious complications such as eyelid drooping or facial paralysis can occur, although this is rare.
- Prescription medications: Anticholinergic medications can cause dry mouth, constipation, drowsiness, and urinary retention in some individuals.
- Surgery: ETS carries a risk of infection, scarring, and nerve damage. In some cases, the procedure may not completely eliminate sweating.
- Iontophoresis: This treatment is generally safe and well-tolerated, but it may cause skin irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals.
- Topical treatments: Antiperspirants can contain harsh chemicals that can irritate the skin. Prescription-strength creams may have side effects such as dryness, itching, or stinging.
- Behavioral therapy: CBT can be a valuable tool for managing hyperhidrosis, but it requires commitment and effort from the individual to achieve results.
It’s essential to discuss any concerns or questions with a qualified healthcare professional before choosing a treatment option for hyperhidrosis.
Botox injections have become a popular treatment option for individuals suffering from hyperhidrosis, also known as excessive sweating. But how do these injections work, and what are the treatment options and alternatives available to those seeking relief from this condition?
According to the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology (2013), Botox injections work by temporarily relaxing the muscles that control sweat glands in the affected area. This relaxation reduces the amount of sweat produced, providing effective relief from excessive sweating.
The active ingredient in Botox, botulinum toxin, works by blocking nerve signals that stimulate sweat gland activity. When injected into the affected area, the toxin causes a temporary reduction in muscle contractions, leading to decreased sweat production.
When it comes to treating hyperhidrosis with Botox injections, there are several factors to consider, including the type of sweating being treated (e.g., palmar or axillary), the severity of sweating, and individual tolerance to the treatment.
In clinical trials, Botox injections have been shown to be effective in reducing excessive sweating in both men and women. One study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that Botox injections resulted in a significant reduction in sweat production, with 75% of participants experiencing complete resolution of symptoms after a single treatment session.
However, while Botox injections have proven to be effective, there are also alternative treatment options available for those seeking relief from hyperhidrosis. One such option is oral medication, specifically anticholinergic agents and beta-blockers, which can help reduce sweat production by targeting the underlying causes of excessive sweating.
Another alternative treatment option is iontophoresis, a non-invasive procedure that uses electrical currents to stimulate sweat glands and remove excess moisture from the skin. This treatment has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms of hyperhidrosis, particularly in patients who have not responded to Botox injections.
In some cases, surgical procedures may also be necessary to address underlying causes of excessive sweating, such as overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism) or nerve damage. In these instances, treatment options may include radioactive iodine therapy, medication, or even surgery to remove affected glands.
It’s worth noting that while Botox injections and alternative treatments can be effective in reducing symptoms of hyperhidrosis, they are not a cure for the condition. Ongoing maintenance treatments may be necessary to maintain results, and it’s essential to work closely with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment.
In addition to these medical options, lifestyle changes can also play an important role in managing excessive sweating. Maintaining a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and avoiding triggers such as caffeine and stress can help reduce symptoms of hyperhidrosis.
Botox for hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by excessive sweating, has become a popular treatment option in recent years.
The American Academy of Dermatology recommends the following treatment options and alternatives:
- Botox Injections: This is the most common treatment for hyperhidrosis. Botox works by temporarily blocking the nerve signals that stimulate sweat glands, resulting in reduced sweating. The procedure involves injecting Botulinum Toxin Type A (Botox) into specific areas of the body, such as the underarms or hands. This can be a highly effective treatment for localized excessive sweating.
- Mirna Therapy: Also known as gene therapy, this treatment involves injecting genes that help to reduce sweat gland activity. It is still an experimental treatment and not yet widely available.
- Iontophoresis: This is a non-invasive treatment that uses a small electrical current to temporarily block nerve signals that stimulate sweat glands. Iontophoresis can be used on specific areas of the body and has been shown to be effective for hyperhidrosis.
- Oral Anticholinergics: These medications work by reducing sweat gland activity in the body. However, they can have side effects such as dry mouth, blurred vision, and urinary retention.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Exercise regularly, but avoid exercising in hot environments to help reduce excessive sweating.
- Avoid triggers that can cause excessive sweating, such as spicy foods or stress.
- Wear loose clothing and use antiperspirants or deodorants to help manage sweat.
- Surgical Options: In some cases, surgical removal of sweat glands (axillary sympathectomy) may be necessary for severe hyperhidrosis. This procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia and can have significant side effects.
It’s essential to consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional to determine the best treatment option for your specific case of hyperhidrosis.
Before starting treatment, it’s crucial to discuss the potential benefits, risks, and alternatives with your healthcare provider.
A comprehensive evaluation will help determine the underlying cause of excessive sweating and identify the most effective treatment approach.
In some cases, a combination of treatments may be recommended for optimal results.
Botox is a popular treatment option for excessive sweating, also known as hyperhidrosis. It has been used for over two decades to effectively reduce sweat production in individuals with this condition.
According to the Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dermatology (2004), Botox works by temporarily blocking the nerve signals that stimulate the sweat glands.
The article explains that botulinum toxin, the active ingredient in Botox, is injected into the affected area under the skin. Once injected, it blocks the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates the sweat glands to produce sweat.
As a result, the sweat glands are unable to produce sweat, leading to a reduction in excessive sweating. The effects of Botox last for several months, typically between 3-4 months, after which time additional injections may be necessary to maintain its effectiveness.
Some of the benefits of using Botox for hyperhidrosis include:
- Effective treatment of excessive sweating in various parts of the body, including the armpits, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet
- No significant side effects or complications reported, although some individuals may experience mild redness, swelling, or bruising at the injection site
- Pain-free procedure that can be performed in a doctor’s office
- Long-lasting results with minimal maintenance required
However, Botox is not suitable for everyone and should only be administered by a qualified healthcare professional. Additionally, it may not be effective for individuals with severe hyperhidrosis or those who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
In some cases, other treatments may be recommended as alternatives to Botox. These include:
- Prescription-strength antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride
- Iontophoresis, a non-invasive treatment that uses low-level electrical currents to reduce sweat production
- Surgical procedures, such as sympathectomy or endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy, which involve cutting or destroying the nerves that control sweat gland activity
It’s worth noting that some studies have shown that Botox can be effective in treating other conditions, including:
- Migraines and tension headaches
- Overactive bladder and urinary incontinence
- Hyperhidrosis of the scalp and face
Overall, while Botox is a highly effective treatment for excessive sweating, it’s essential to weigh its benefits against any potential risks or side effects and discuss alternative options with a qualified healthcare professional.
Botox injections are a popular treatment option for hyperhidrosis, also known as excessive sweating, affecting over 2% of the population in the United States alone.
Understandably, individuals seeking relief from this condition often explore various treatment alternatives to traditional Botox injections. In this article, we will delve into the treatment options and alternatives available for hyperhidrosis, as well as provide an overview of the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval process for medical treatments.
**Treatment Options:**
1. **Botox Injections**: Botox is a neurotoxin protein that temporarily relaxes muscles, reducing sweat gland activity. Injected into specific areas, it can effectively treat hyperhidrosis in underarms, palms, soles, and other affected regions.
2. **Iontophoresis**: This non-invasive treatment uses electrical currents to temporarily block the nerve signals that stimulate sweating glands. It is a popular alternative for those who prefer not to undergo injections or have concerns about long-term effects.
3. **Oral Antiperspirants**: Prescription-strength oral antiperspirants can help reduce sweat production. However, their effectiveness varies from person to person, and they may not address the underlying causes of hyperhidrosis.
4. **MiraDry**: This non-surgical procedure uses microwave energy to destroy the sweat glands, providing long-term relief from excessive sweating. While it has shown promising results, more research is needed to fully understand its effects on long-term health.
**Treatment Alternatives:**
1. **Prescription Strength Antiperspirants**: Over-the-counter antiperspirants with higher aluminum content may be more effective than their non-prescription counterparts for those who experience excessive sweating.
2. **Sweat-Reducing Creams and Sprays**: Topical creams and sprays containing ingredients like aluminum chloride, salicylic acid, or tea tree oil can help reduce sweat production. However, their effectiveness may be limited by skin sensitivity and individual response to these substances.
3. **Natural Remedies**: Certain natural remedies such as apple cider vinegar, cinnamon, and mint have been reported to help reduce sweating in some individuals. While these methods may be beneficial for mild cases, they often require consistent effort and patience.
**FDA Approval Process:**
The FDA plays a crucial role in approving medical treatments for hyperhidrosis. To be approved by the agency, new treatments must undergo rigorous testing to demonstrate safety and efficacy in treating excessive sweating.
FDA approval is typically granted under the following categories:
1. **Class I**: Low-risk treatments with substantial evidence supporting their effectiveness.
2. **Class II**: Moderate-risk treatments with moderate evidence of effectiveness.
3. **Class III**: High-risk treatments with limited or inadequate evidence of effectiveness.
Understanding the treatment options, alternatives, and FDA approval process for hyperhidrosis is essential for making informed decisions about the best course of treatment. Consultation with a healthcare professional can help determine the most effective approach for individual cases of excessive sweating.
The National Hyperhidrosis Society offers various treatment options and alternatives for individuals suffering from excessive sweating, including Botox injections.
Botulinum toxin type A (Botox) is a neurotoxin protein that temporarily relaxes muscles, thereby reducing sweat gland activity in the treated area. In the context of hyperhidrosis, Botox injections are administered to block the nerve signals that stimulate sweat glands, resulting in a reduction in sweating.
The most commonly used treatment areas for Botox injections in hyperhidrosis patients include underarms, palms of the hands, soles of the feet, and facial areas such as the forehead, nose, and chin. A single session typically involves injecting Botox into specific areas using a fine needle, with a total dose ranging from 100 to 200 units.
The effects of Botox injections typically begin within two weeks after treatment and can last for several months, with some studies suggesting up to six months. However, the duration of effect depends on individual factors, such as skin type, muscle tone, and sweating patterns.
Alternatives to Botox injections include other treatments like oral medications, iontophoresis, and topical creams or ointments. Oral medications, such as anticholinergics (e.g., glycopyrrolate) or beta-blockers (e.g., propranolol), can help reduce sweating by altering the body’s natural sweat-regulation mechanisms.
Iontophoresis is a non-invasive procedure that uses a low-voltage electrical current to temporarily paralyze the sweat glands, reducing sweat production. This treatment involves placing metal plates under the armpits or on other affected areas and applying an ion-rich solution to stimulate the electrical response.
Topical creams or ointments containing aluminum chloride can help reduce sweating by causing a temporary vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels) in the treated area, reducing sweat gland activity. These products are available over-the-counter or through prescription and come in various concentrations and formulations.
In addition to these treatments, lifestyle modifications such as avoiding triggers that exacerbate sweating, wearing loose-fitting clothing, and staying cool in hot environments can help manage symptoms of hyperhidrosis.
Some patients may also consider combining multiple treatment options for optimal results. For example, using Botox injections in conjunction with oral medications or topical creams can provide a more comprehensive approach to managing excessive sweating.
Book Your Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige Today
It’s essential for individuals struggling with hyperhidrosis to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist to determine the most suitable treatment plan for their specific condition and needs. With the right guidance, effective management of hyperhidrosis is possible, improving quality of life and overall well-being.
Botox injections have become a popular treatment option for excessive sweating, also known as hyperhidrosis. The European Journal of Surgery published an article in 2018 discussing the various treatment options and alternatives available for this condition.
The article highlights the use of botulinum toxin type A (Botox) as a first-line treatment for mild to moderate primary axillary hyperhidrosis, also known as underarm sweating. Botox works by temporarily blocking nerve signals that stimulate sweat glands, reducing sweat production in affected areas.
For more severe cases of hyperhidrosis, other treatments may be necessary. One alternative is surgery, which involves removing or destroying the sweat glands responsible for excessive sweating. This procedure, known as thoracoscopic sympathectomy, can be performed using minimally invasive techniques and has a high success rate in reducing sweat production.
Another treatment option is topical treatments, such as aluminum chloride, which are applied directly to the affected area to reduce sweat production. However, these treatments may have limitations and can be time-consuming to apply regularly.
Oral medications, such as anticholinergic agents, are also available to treat hyperhidrosis. These medications work by blocking nerve signals that stimulate sweat glands, but they may have side effects and require regular dosing.
In addition to these medical treatments, lifestyle modifications can help manage excessive sweating. These include avoiding triggers such as heat, stress, and certain foods, staying hydrated, and wearing loose-fitting clothing.
Other alternative therapies that have been used to treat hyperhidrosis include acupuncture, herbal supplements, and reflexology. While some people claim these treatments are effective, there is limited scientific evidence to support their use for this condition.
A comprehensive treatment plan should be developed in consultation with a healthcare professional, taking into account the individual’s specific needs and circumstances. It’s also essential to weigh the pros and cons of each treatment option and alternative therapy before making an informed decision.
For patients who are interested in undergoing surgery or other medical procedures, it’s crucial to carefully evaluate the risks and benefits associated with these treatments. This includes discussing potential complications, side effects, and long-term outcomes with a qualified healthcare provider.
In some cases, combining multiple treatment options may be necessary to achieve optimal results. For example, using Botox injections in conjunction with lifestyle modifications or oral medications may lead to better symptom control than using only one treatment approach.
The article emphasizes the importance of personalized treatment planning and ongoing monitoring to ensure the effectiveness and safety of hyperhidrosis treatments. By considering a range of options and alternatives, individuals can work with their healthcare provider to develop an effective treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and circumstances.
Read more about Alabama Sig Delt here. Read more about Raindrops and Ribbons here. Read more about Melissa J Design here. Read more about MS Style and Grace here. Read more about One One Three Online here.
- What Is Russian Lip Filler - November 12, 2025
- Weed Drinks That Won’t Leave You Couch Locked - November 10, 2025
- Under Eye Rejuvenation In Frensham, Surrey - November 7, 2025
